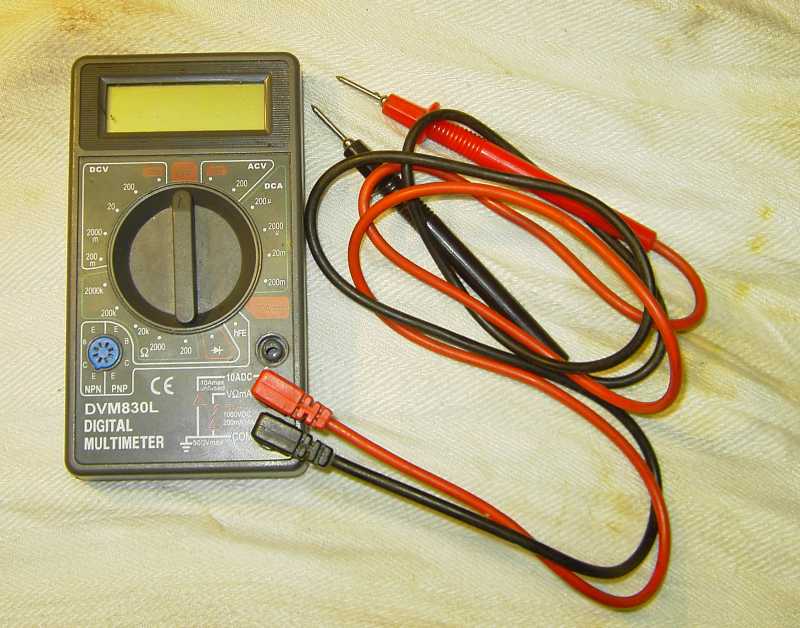
Voltmeter Digital instruments can be bought cheap in most hardware stores, and are generally god enough for home / hobby use Voltage
(V)
|
|
|
On older systems it is direct current (dc) in question. Usually measurement is between chassis and a component, like a dynamo, - the voltmeters black (-) lead on chassis, and the red lead (+) on the dynamo's D terminal. Always
set the voltmeter range higher than what is expected to see. (dc 20V) Current is measured in ampere
(A) Here
again it is dirrect current (dc) it is, though, doubtful, if the cheap
instruments can handle the current for, for instance the main bulb. Always
set the voltmeter range higher than what is expected to see. Smallest
usefull range is 10 A dc Resistance is measured in Ohm (W)
Can
be used to measure connection not to be uses with power on the system, the
voltmeter can be damaged. Remove one of the battery leads . You
can measure if a dynamo armature windings is broken, but normally not a shorting. Here the small ranges are recommended (X1 or X10). The high range are so sensitive, that you are able to measure the connection through your fingers. KW
(kilo ohm) means 1000 ohm, MW
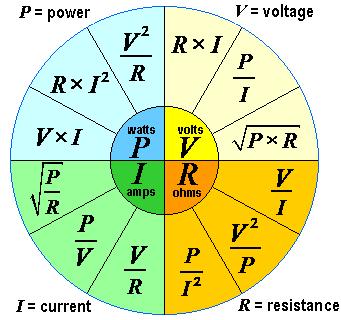
(Mega-ohm) means million ohm. Power
is called Watt
(W) Normally
not measured, but calculated. Volt
times ampere gives Watt (V x A = W) and the other way Watt
divided Volt gives ampere (W / V = A). Useful
for calculating how much current there are on hand. If
you have a 45 W main bulb, 5 W in the rear, and battery ignition that use 15 W
(typical), you all together use 65 W. Then you don't get far with a 45 W dynamo. And The 45 W is what it can give, not necessarily what it gives, when you stroll along
|
|
|
|
Ohms law As to be seen
|
||||||||||||||||